Postbiotics
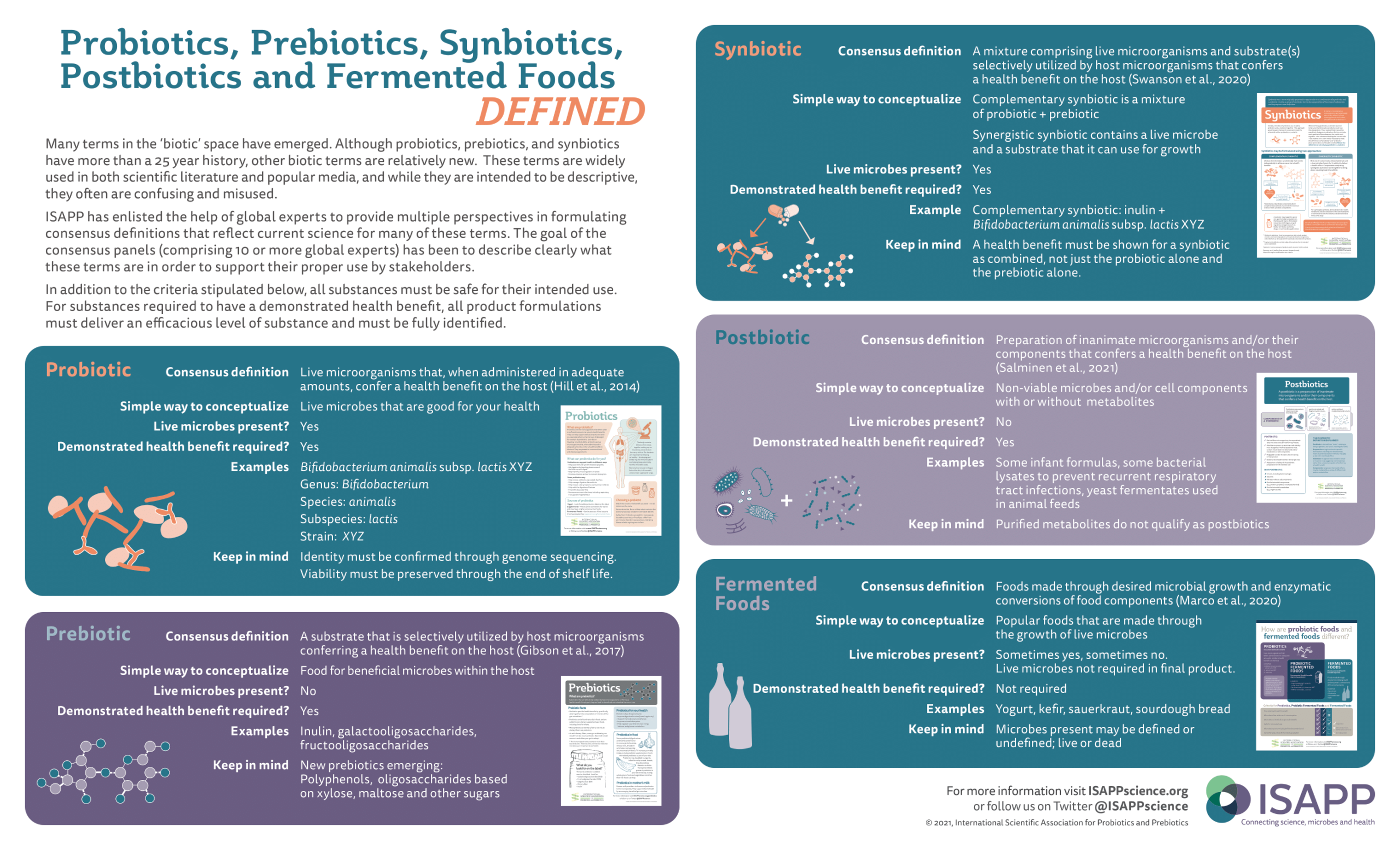
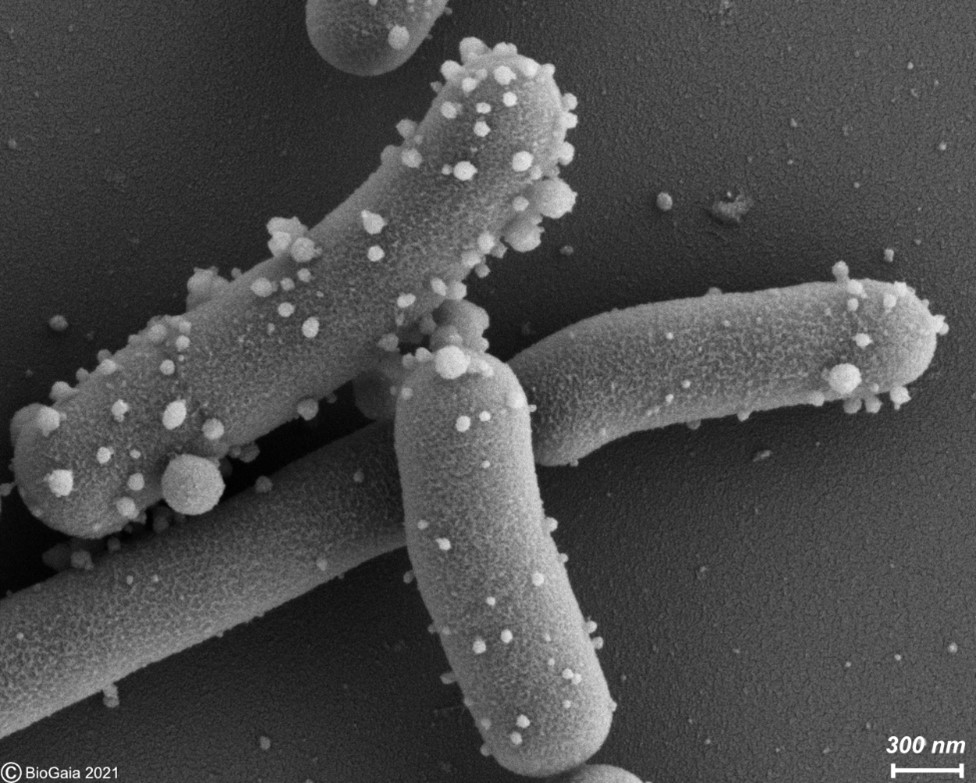
Postbiotics contain inactivated microbial cells or cell components, with or without metabolites.
Postbiotics contain inactivated microbial cells or cell components, with or without metabolites.
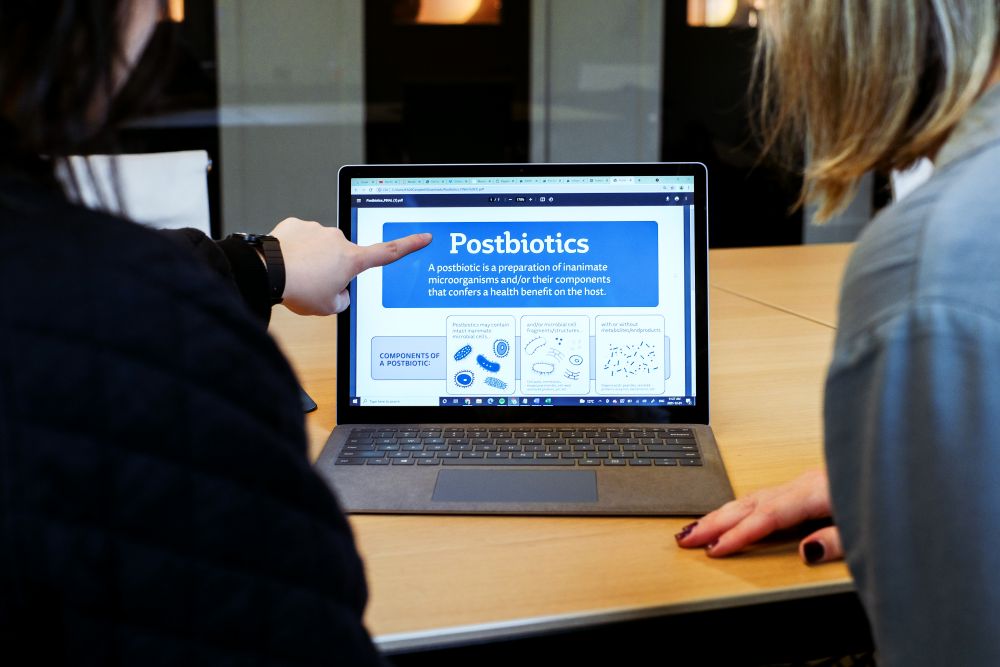
Microbes don’t have to be alive to have health benefits. A postbiotic is a preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host — in other words, whole or partial non-living microbes that can be consumed for their contribution to our health.
Postbiotics are often confused with metabolites (molecules produced by living microorganisms), but in reality metabolites by themselves do not qualify as postbiotics. To create a postbiotic, the living microbial cells must be deliberately killed or inactivated, and parts of the cells must remain in the preparation. The study of postbiotics is progressing rapidly within the field of biotics.